Uncrossed Lines
We write the integers of A and B (in the order they are given) on two separate horizontal lines.
Now, we may draw connecting lines: a straight line connecting two numbers A[i] and B[j] such that:
A[i] == B[j];- The line we draw does not intersect any other connecting (non-horizontal) line.
Note that a connecting lines cannot intersect even at the endpoints: each number can only belong to one connecting line.
Return the maximum number of connecting lines we can draw in this way.
Example 1:
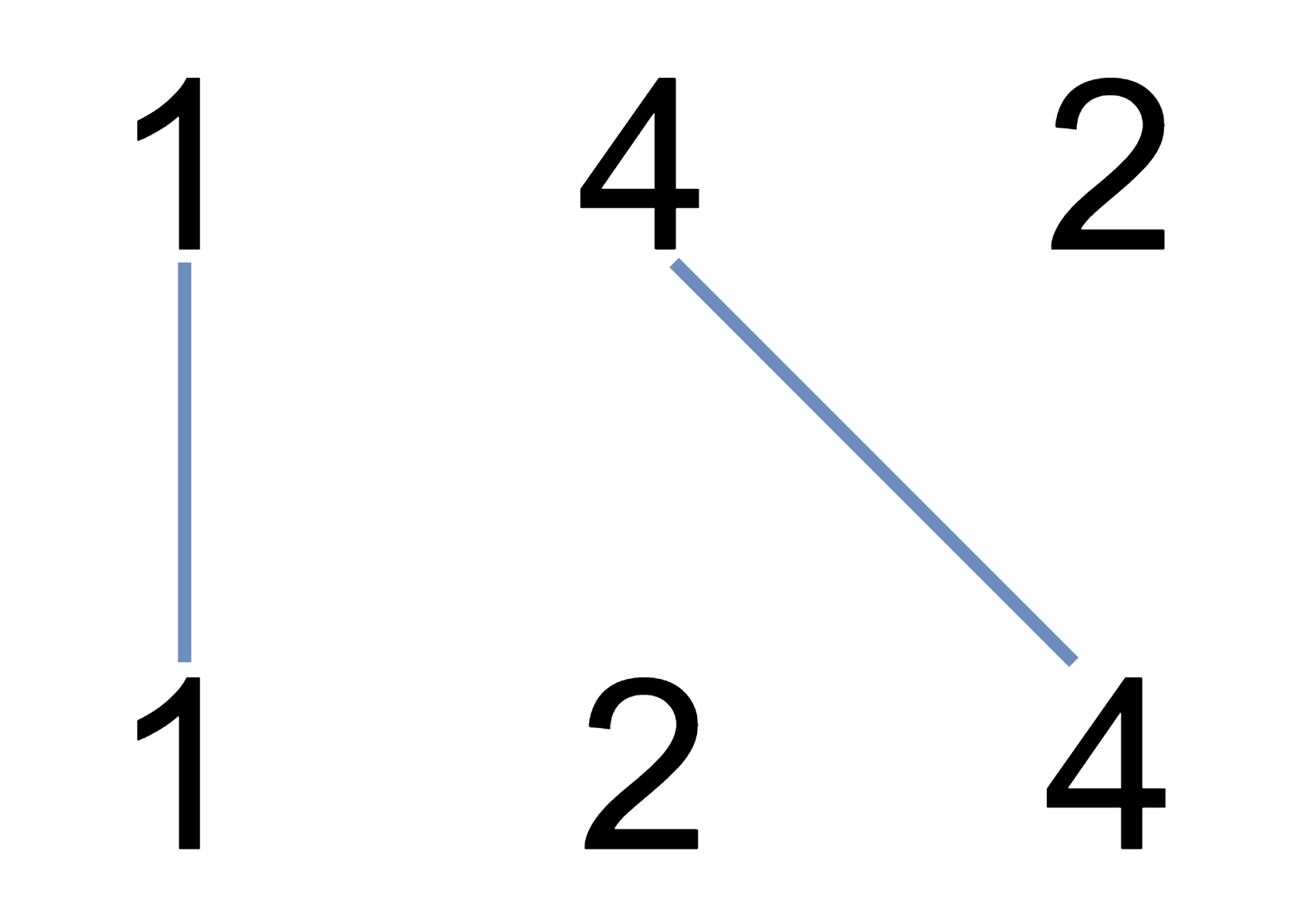
Input: A = [1,4,2], B = [1,2,4] Output: 2 Explanation: We can draw 2 uncrossed lines as in the diagram. We cannot draw 3 uncrossed lines, because the line from A[1]=4 to B[2]=4 will intersect the line from A[2]=2 to B[1]=2.
Example 2:
Input: A = [2,5,1,2,5], B = [10,5,2,1,5,2] Output: 3
Example 3:
Input: A = [1,3,7,1,7,5], B = [1,9,2,5,1] Output: 2
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 5001 <= B.length <= 5001 <= A[i], B[i] <= 2000
class Solution {
public:
int maxUncrossedLines(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) {
int n=A.size(),m=B.size();
int dp[n+1][m+1];
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
for(int j=1;j<=m;++j)
{
if(A[i-1]==B[j-1])
{
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}else{
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[n][m];
}
};





