Interval List Intersections
Given two lists of closed intervals, each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
(Formally, a closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b. The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that is either empty, or can be represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].)
Example 1:
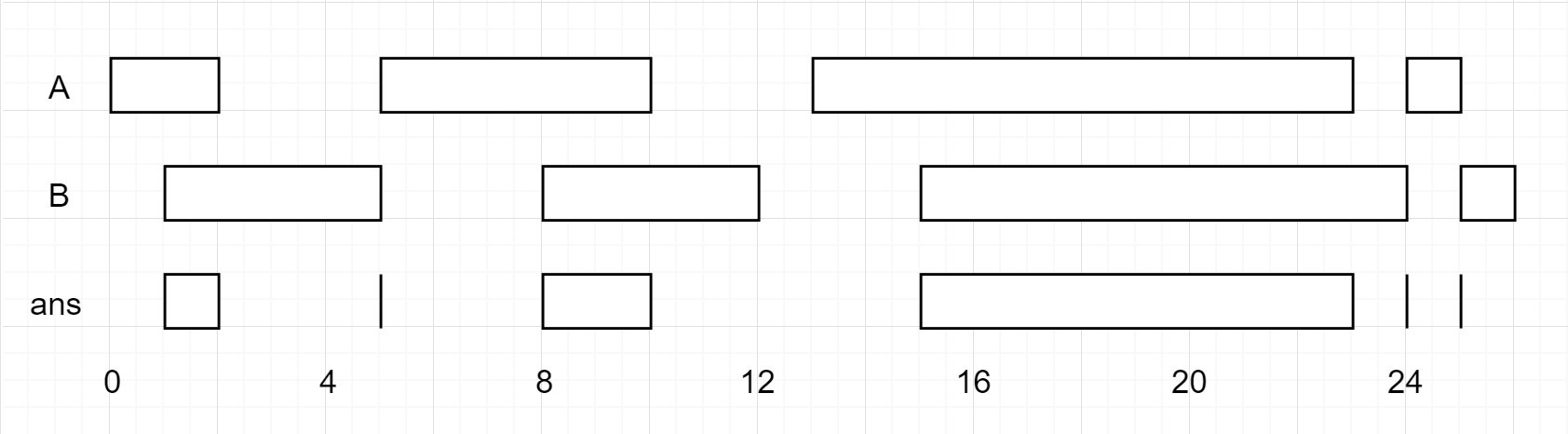
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Note:
0 <= A.length < 10000 <= B.length < 10000 <= A[i].start, A[i].end, B[i].start, B[i].end < 10^9
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& A, vector<vector<int>>& B)
{
vector<vector<int> > ans;
int n=A.size(),m=B.size();
int i=0,j=0;
while(i<n&&j<m)
{
if(A[i][0]<=B[j][1]&&A[i][1]>=B[j][0])
{
ans.push_back({max(A[i][0],B[j][0]),min(A[i][1],B[j][1])});
}
if(A[i][1]<B[j][1])
++i;
else
++j;
}
return ans;
}
};




